Impulse and Change in Momentum
Impulse and Change in Momentum: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Linear Impulse, Linear Impulse from F-T Diagrams, Linear Impulse of Time Varying Force and, Linear Impulse of Constant Force
Important Questions on Impulse and Change in Momentum
A bullet of leaves the barrel of gun with a velocity of . If the barrel of gun is long and mass of gun is then value of impulse supplied to the gun will be:
A ball of mass dropped from a height of strikes a horizontal floor and rebounds to a height of . Find the impulse exerted by the floor on the ball during impact.
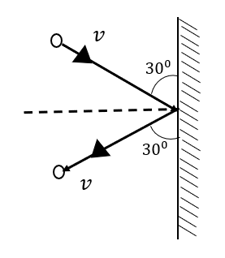
A particle of mass strikes a wall with speed at an angle with the wall elastically as shown in the figure. Calculate the impulse imparted to the ball by the wall.
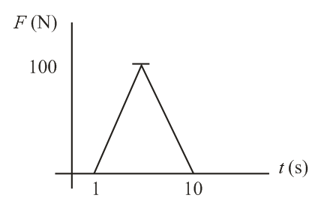
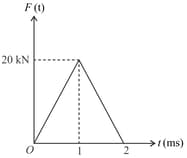
What is the impulse of force shown in the figure?
A force varying with time acts on a particle moving along axis. Starting from particle is taken along axis. Find the momentum of particle at .
ball thrown with a velocity of the left after a collision with the wall the ball is reflected with a velocity of to the right. Determine the impulse
A time varying force acts on a ball of mass for . The force versus time curve is shown below. If the initial speed of the ball is , then the speed of ball after is
A smooth sphere of mass moving with a horizontal speed strikes at right angle a vertical wall and bounces off the wall with a horizontal speed .The coefficient of restitution between the sphere and the wall and the impulses exerted on the wall at impact?
A cannon of mass starts sliding freely down a smooth inclined plane at an angle to the horizontal. After the cannon covered the distance , a shot was fired, the shell leaving the cannon in the horizontal direction with a momentum . As a consequence, the cannon stopped instantly. Assuming the change in mass of the canon to be negligible due to shot, determine the duration of the shot.
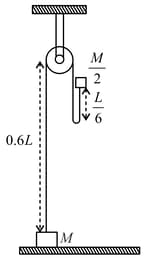
A block of mass at rest on the floor is attached to a ball of mass via a light inextensible string of length which passes over a light small frictionless pulley. The pulley is at a height of from the floor. The ball is raised to a height of and released (see figure). The speed of the block at the instant the string gets taut (not slack) will be
A carrom coin of radius and mass strikes the side of the board at an angle with respect to the normal. The coin stays in contact with the side for and rebounds at an angle of with respect to the normal. The initial speed of the coin is and its final speed is . The average impulsive force on the coin in the normal direction is about
An object with a mass moves at a constant velocity of . A constant force then acts for second on the object and gives it a speed of in opposite direction. Calculate the impulse acting on it.
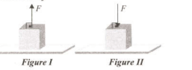
When the force Facts on the weight Gas in Figure 1, the reaction force of the ground becomes N, and when the force is reversed as in Figure II, the reaction force of the ground becomes N,
Since what is the value of .
A body of mass is acted upon by a net force which varies with time as shown in the figure. Then the net momentum in units gained by the body at the end is
A ball of drops vertically on the floor with a speed of . It rebounds with a velocity of .
What impulse acts on the ball during contact?
A hammer weighing strikes the head of a nail with a speed of and drives it into the wall. The impulse imparted to the wall is
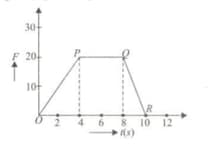
A force-time graph for a linear motion is shown in following figure. The segments shown are circular. The linear momentum gained between 0 and 8 seconds is:
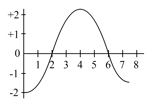
Starting from rest, a car moves with a constant acceleration, and comes to a momentary stop with the same constant deceleration. Subsequently, it reverses its motion and returns to its original position in a similar manner. Which one of the following graphs of momentum versus time best describes the motion of the car?
Two billiard ball each of mass moving in opposite directions with speed collide and rebounds with the same speed. The magnitude of impulse imparted to each ball due to other is
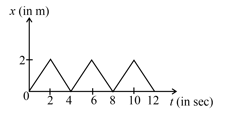
Figure shows the position–time graph of one dimensional motion of a body of mass . What is the time interval between two consecutive impulses received by the body?